
Understanding PCOS: Causes, Complications, and Ways to Manage It
Understanding PCOS: Causes, Complications, and Ways to Manage It
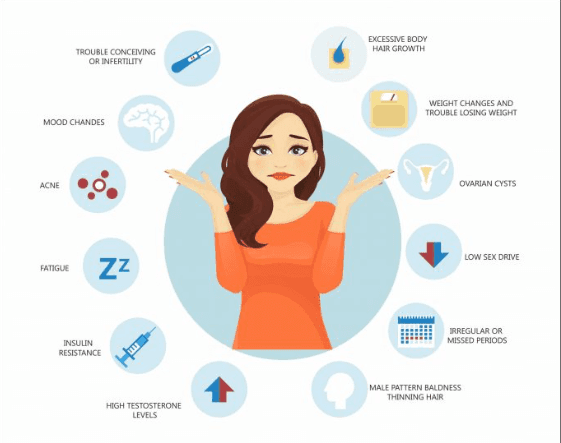

What is PCOS?
PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances that result in:
Menstrual irregularities: Infrequent or prolonged periods.
Excess androgen levels: High levels of male hormones leading to symptoms like hirsutism (excess hair growth), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
Ovarian dysfunction: The ovaries may develop numerous small fluid-filled follicles and fail to release eggs regularly.
PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances that result in:
Menstrual irregularities: Infrequent or prolonged periods.
Excess androgen levels: High levels of male hormones leading to symptoms like hirsutism (excess hair growth), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
Ovarian dysfunction: The ovaries may develop numerous small fluid-filled follicles and fail to release eggs regularly.
PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances that result in:
Menstrual irregularities: Infrequent or prolonged periods.
Excess androgen levels: High levels of male hormones leading to symptoms like hirsutism (excess hair growth), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
Ovarian dysfunction: The ovaries may develop numerous small fluid-filled follicles and fail to release eggs regularly.
Symptoms of PCOS
Women with PCOS may experience:
Irregular or absent periods.
Excessive hair growth on the face, chest, or back.
Acne and oily skin.
Weight gain or obesity
Women with PCOS may experience:
Irregular or absent periods.
Excessive hair growth on the face, chest, or back.
Acne and oily skin.
Weight gain or obesity
Women with PCOS may experience:
Irregular or absent periods.
Excessive hair growth on the face, chest, or back.
Acne and oily skin.
Weight gain or obesity
Causes of PCOS
While the exact cause of PCOS remains unknown, several factors contribute to its development:
1. Excess Insulin
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps the body use sugar for energy. When cells become resistant to insulin, blood sugar levels rise, prompting the body to produce more insulin. This excess insulin may increase androgen production, which disrupts ovulation.
2. Excess Androgen
Abnormally high levels of androgen hormones are produced by the ovaries, causing symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
While the exact cause of PCOS remains unknown, several factors contribute to its development:
1. Excess Insulin
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps the body use sugar for energy. When cells become resistant to insulin, blood sugar levels rise, prompting the body to produce more insulin. This excess insulin may increase androgen production, which disrupts ovulation.
2. Excess Androgen
Abnormally high levels of androgen hormones are produced by the ovaries, causing symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
While the exact cause of PCOS remains unknown, several factors contribute to its development:
1. Excess Insulin
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps the body use sugar for energy. When cells become resistant to insulin, blood sugar levels rise, prompting the body to produce more insulin. This excess insulin may increase androgen production, which disrupts ovulation.
2. Excess Androgen
Abnormally high levels of androgen hormones are produced by the ovaries, causing symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
Complications of PCOS
Untreated PCOS can lead to serious health complications, including:
Infertility: Difficulty in conceiving due to irregular ovulation.
Gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure: During pregnancy, these conditions can pose risks to both mother and baby.
Miscarriage or premature birth: Increased likelihood of complications during pregnancy.
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Severe liver inflammation caused by fat accumulation.
Metabolic Syndrome: A combination of conditions like high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, increasing cardiovascular risks.
Type 2 Diabetes or Prediabetes: Chronic blood sugar imbalances.
Sleep Apnea: Interrupted breathing during sleep, common in overweight women with PCOS.
Mental Health Issues: Depression, anxiety, and eating disorders are prevalent among women with PCOS.
Untreated PCOS can lead to serious health complications, including:
Infertility: Difficulty in conceiving due to irregular ovulation.
Gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure: During pregnancy, these conditions can pose risks to both mother and baby.
Miscarriage or premature birth: Increased likelihood of complications during pregnancy.
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Severe liver inflammation caused by fat accumulation.
Metabolic Syndrome: A combination of conditions like high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, increasing cardiovascular risks.
Type 2 Diabetes or Prediabetes: Chronic blood sugar imbalances.
Sleep Apnea: Interrupted breathing during sleep, common in overweight women with PCOS.
Mental Health Issues: Depression, anxiety, and eating disorders are prevalent among women with PCOS.
Untreated PCOS can lead to serious health complications, including:
Infertility: Difficulty in conceiving due to irregular ovulation.
Gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure: During pregnancy, these conditions can pose risks to both mother and baby.
Miscarriage or premature birth: Increased likelihood of complications during pregnancy.
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Severe liver inflammation caused by fat accumulation.
Metabolic Syndrome: A combination of conditions like high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, increasing cardiovascular risks.
Type 2 Diabetes or Prediabetes: Chronic blood sugar imbalances.
Sleep Apnea: Interrupted breathing during sleep, common in overweight women with PCOS.
Mental Health Issues: Depression, anxiety, and eating disorders are prevalent among women with PCOS.
Managing PCOS: Lifestyle Modifications
While PCOS has no definitive cure, lifestyle changes can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve overall health.
1. Regular Exercise
Engage in aerobic exercises for at least 30 minutes, 5–6 days a week. Benefits include:
Improved insulin sensitivity.
Better cholesterol levels and body composition.
Weight loss, which reduces androgen levels and promotes ovulation.
2. Healthy Dietary Modifications
Making smart food choices can help manage PCOS effectively:
Focus on High-Fiber Foods
Foods high in fiber slow digestion and reduce insulin resistance.
Examples: Whole grains, lentils, beans, and fresh vegetables.
Adopt the DASH Diet
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet reduces heart disease risks and focuses on:
Fish, poultry, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
Avoiding saturated fats, added sugars, and processed foods.
Avoid These Foods
Processed snacks and sugary beverages.
Refined carbohydrates like white bread and pastries.
While PCOS has no definitive cure, lifestyle changes can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve overall health.
1. Regular Exercise
Engage in aerobic exercises for at least 30 minutes, 5–6 days a week. Benefits include:
Improved insulin sensitivity.
Better cholesterol levels and body composition.
Weight loss, which reduces androgen levels and promotes ovulation.
2. Healthy Dietary Modifications
Making smart food choices can help manage PCOS effectively:
Focus on High-Fiber Foods
Foods high in fiber slow digestion and reduce insulin resistance.
Examples: Whole grains, lentils, beans, and fresh vegetables.
Adopt the DASH Diet
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet reduces heart disease risks and focuses on:
Fish, poultry, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
Avoiding saturated fats, added sugars, and processed foods.
Avoid These Foods
Processed snacks and sugary beverages.
Refined carbohydrates like white bread and pastries.
While PCOS has no definitive cure, lifestyle changes can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve overall health.
1. Regular Exercise
Engage in aerobic exercises for at least 30 minutes, 5–6 days a week. Benefits include:
Improved insulin sensitivity.
Better cholesterol levels and body composition.
Weight loss, which reduces androgen levels and promotes ovulation.
2. Healthy Dietary Modifications
Making smart food choices can help manage PCOS effectively:
Focus on High-Fiber Foods
Foods high in fiber slow digestion and reduce insulin resistance.
Examples: Whole grains, lentils, beans, and fresh vegetables.
Adopt the DASH Diet
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet reduces heart disease risks and focuses on:
Fish, poultry, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
Avoiding saturated fats, added sugars, and processed foods.
Avoid These Foods
Processed snacks and sugary beverages.
Refined carbohydrates like white bread and pastries.
Seek Expert Guidance
If you’re struggling with PCOS, consulting a professional dietitian can make a significant difference in managing your condition.
Contact Neha's Diet Counseling Facility
Email: nehatgore@gmail.com
Call or WhatsApp: 9881099705
If you’re struggling with PCOS, consulting a professional dietitian can make a significant difference in managing your condition.
Contact Neha's Diet Counseling Facility
Email: nehatgore@gmail.com
Call or WhatsApp: 9881099705
If you’re struggling with PCOS, consulting a professional dietitian can make a significant difference in managing your condition.
Contact Neha's Diet Counseling Facility
Email: nehatgore@gmail.com
Call or WhatsApp: 9881099705
Take Control of Your Health
With the right knowledge and consistent lifestyle changes, living with PCOS can become more manageable. Don’t let PCOS define your life—start your journey towards better health today!
Let's get to know each other.
Let's get to know each other.
Let's get to know each other.
